Global plastics summit starts as COP29 ends
Negotiators gathering in South Korea seek an end to the world's plastic pollution crisis, though Trump's election may muddle the deal


What happened
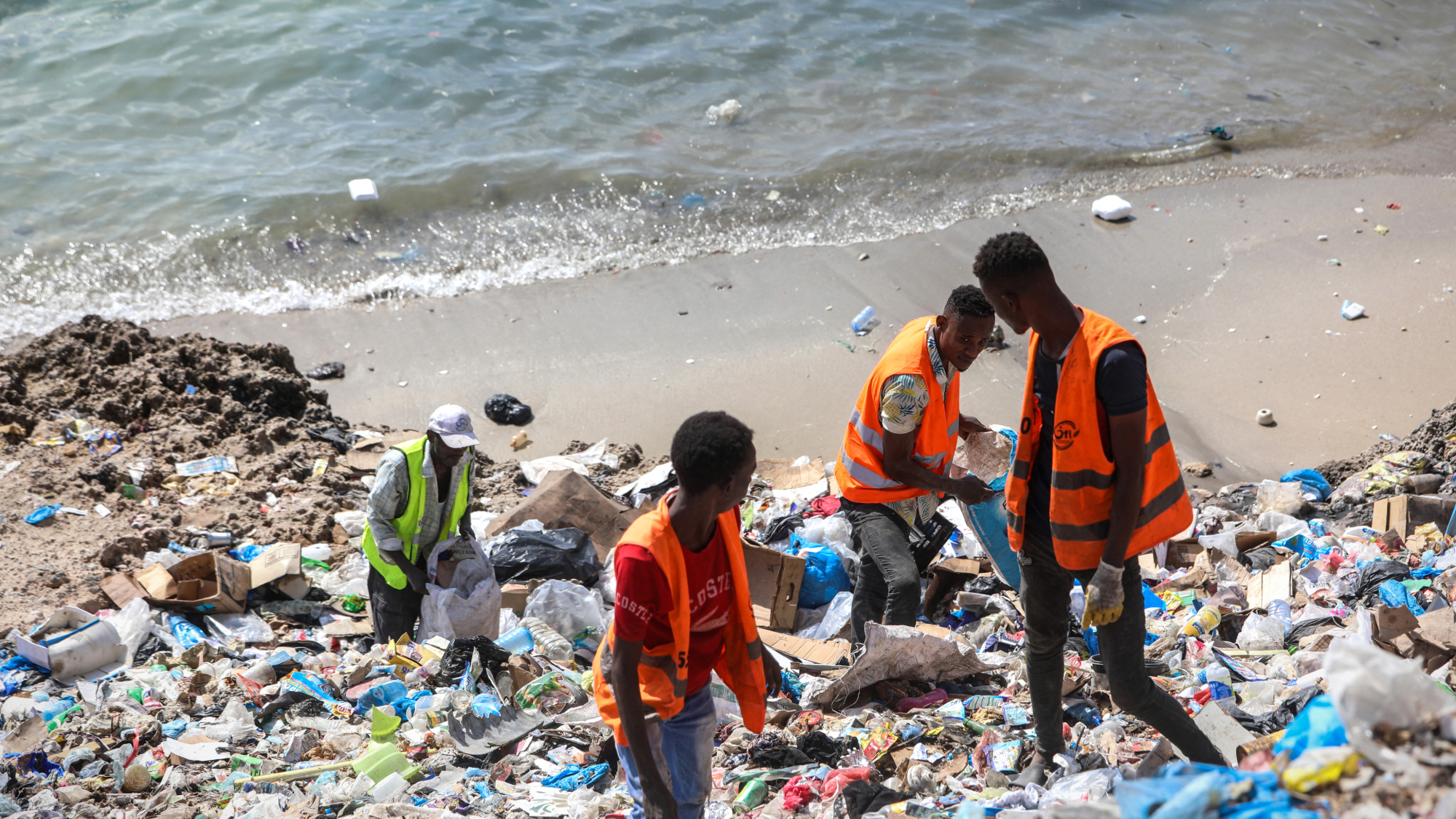
The United Nations–sponsored COP29 climate talks ended in Baku, Azerbaijan, Sunday with approval of a deal to provide $300 billion a year to fight climate change, focused on helping poorer countries manage the rise in global temperatures. Negotiators gather Monday in Busan, South Korea, to work on hammering out a landmark deal to manage the world's plastics crisis.
Who said what
Delegates from 175 countries are in Busan for the "fifth and ostensibly final" meeting to curb plastic pollution, but "lingering divisions cast doubts on whether a final agreement is in sight," Reuters said. The European Union and 66 countries are looking for a treaty to cap and reduce the amount of plastic produced, and the U.S. "raised eyebrows in August" when it agreed to back those caps."
"Then came the election of Donald J. Trump," The New York Times said. Now "few expect the United States to sign on to an eventual treaty at all," with Trump siding with the petrochemical companies and other plastic-producing nations that oppose reducing output. Microplastics are already in drinking water, fish and animals, and even human organs, but plastics companies at the summit argue that the goal should be reducing waste through reuse and recycling.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
COP29's final deal "rescued the summit from near collapse," but it left "just about everyone frustrated," Semafor said. Even the "disappointing" $300 billion number will be hard to turn from dollars in a ledger into "hard cash in the hands of the most climate-vulnerable countries."
What next?
Many developing countries, already "angered by the modest deal on climate crisis financing," argued that an "ambitious" plastics treaty with holdouts is "better than a watered-down one signed by all," the Times said. The Busan summit ends Saturday.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
-
 San Francisco tackles affordability problems with free child care
San Francisco tackles affordability problems with free child careThe Explainer The free child care will be offered to thousands of families in the city
-
 How realistic is the Democratic plan to retake the Senate this year?
How realistic is the Democratic plan to retake the Senate this year?TODAY’S BIG QUESTION Schumer is growing bullish on his party’s odds in November — is it typical partisan optimism, or something more?
-
 Taxes: It’s California vs. the billionaires
Taxes: It’s California vs. the billionairesFeature Larry Page and Peter Thiel may take their wealth elsewhere
-
 The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.
The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.Under the radar It is quickly melting away
-
 How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whales
How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whalesUnder the radar Monitoring the sea in the air
-
 ‘Jumping genes’: how polar bears are rewiring their DNA to survive the warming Arctic
‘Jumping genes’: how polar bears are rewiring their DNA to survive the warming ArcticUnder the radar The species is adapting to warmer temperatures
-
 Environment breakthroughs of 2025
Environment breakthroughs of 2025In Depth Progress was made this year on carbon dioxide tracking, food waste upcycling, sodium batteries, microplastic monitoring and green concrete
-
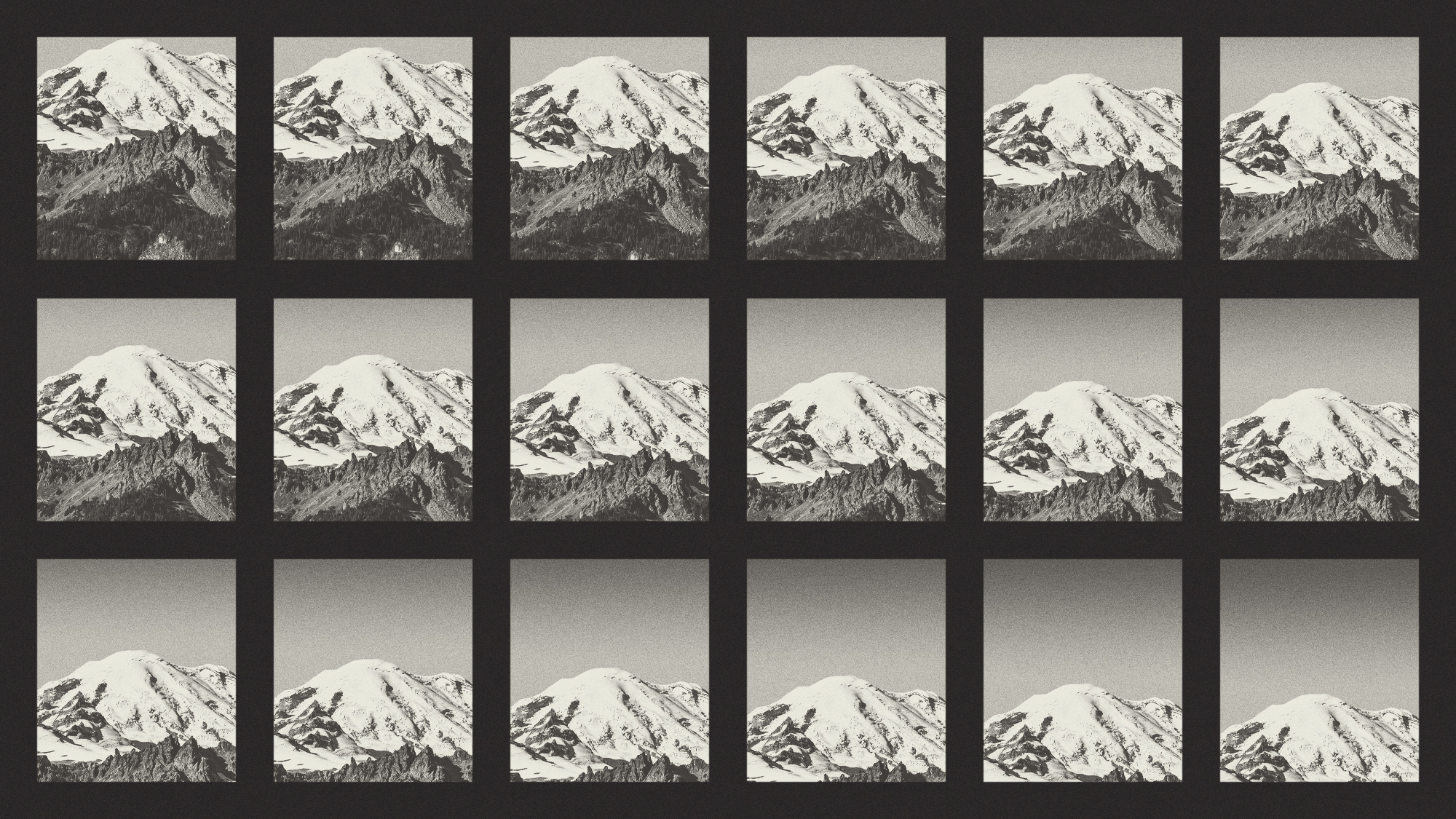 Crest falling: Mount Rainier and 4 other mountains are losing height
Crest falling: Mount Rainier and 4 other mountains are losing heightUnder the radar Its peak elevation is approximately 20 feet lower than it once was
-
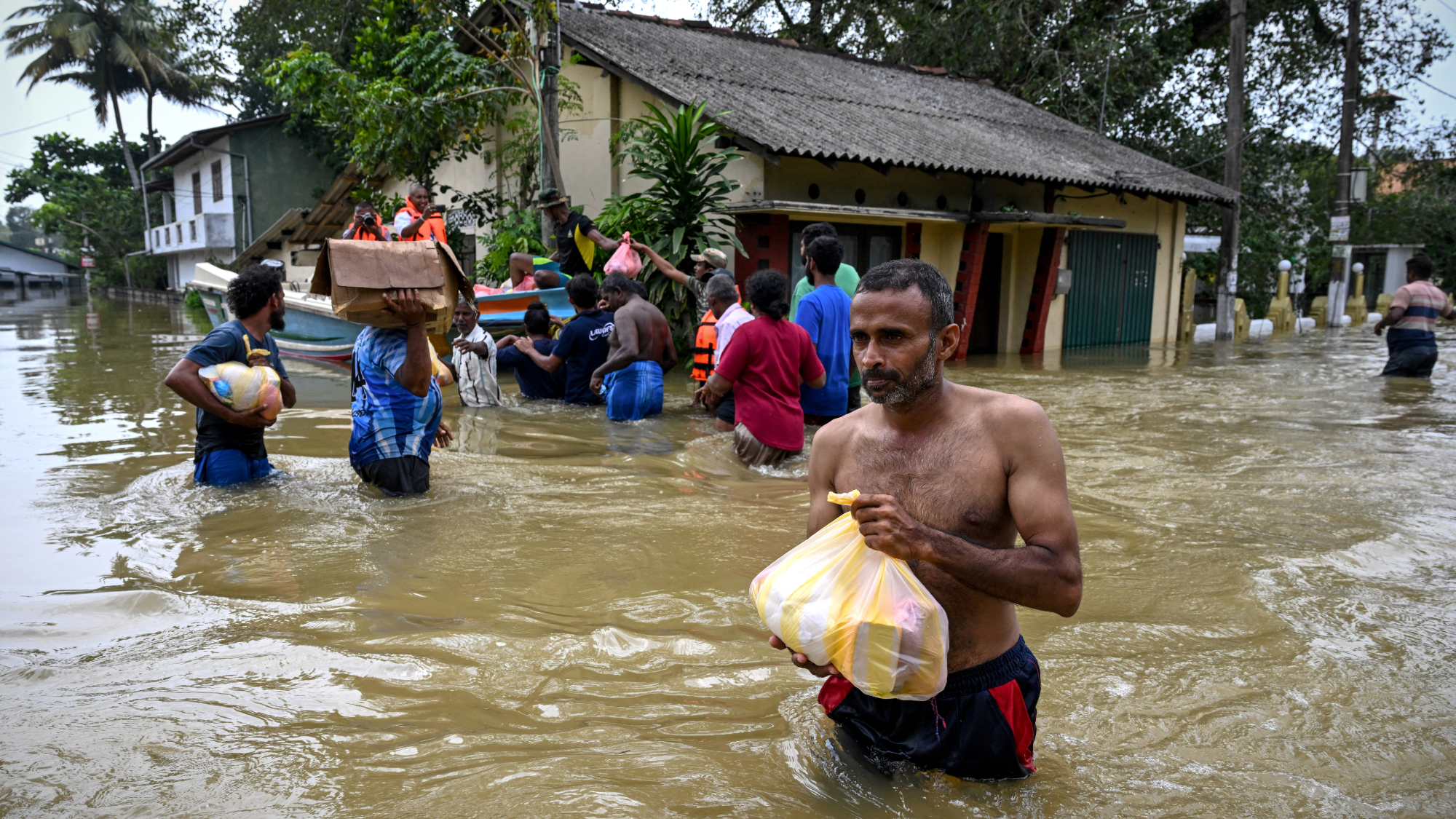 Death toll from Southeast Asia storms tops 1,000
Death toll from Southeast Asia storms tops 1,000speed read Catastrophic floods and landslides have struck Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Thailand and Malaysia
-
 Can for-profit geoengineering put a pause on climate change?
Can for-profit geoengineering put a pause on climate change?In the Spotlight Stardust Solutions wants to dim the sun. Scientists are worried.
-
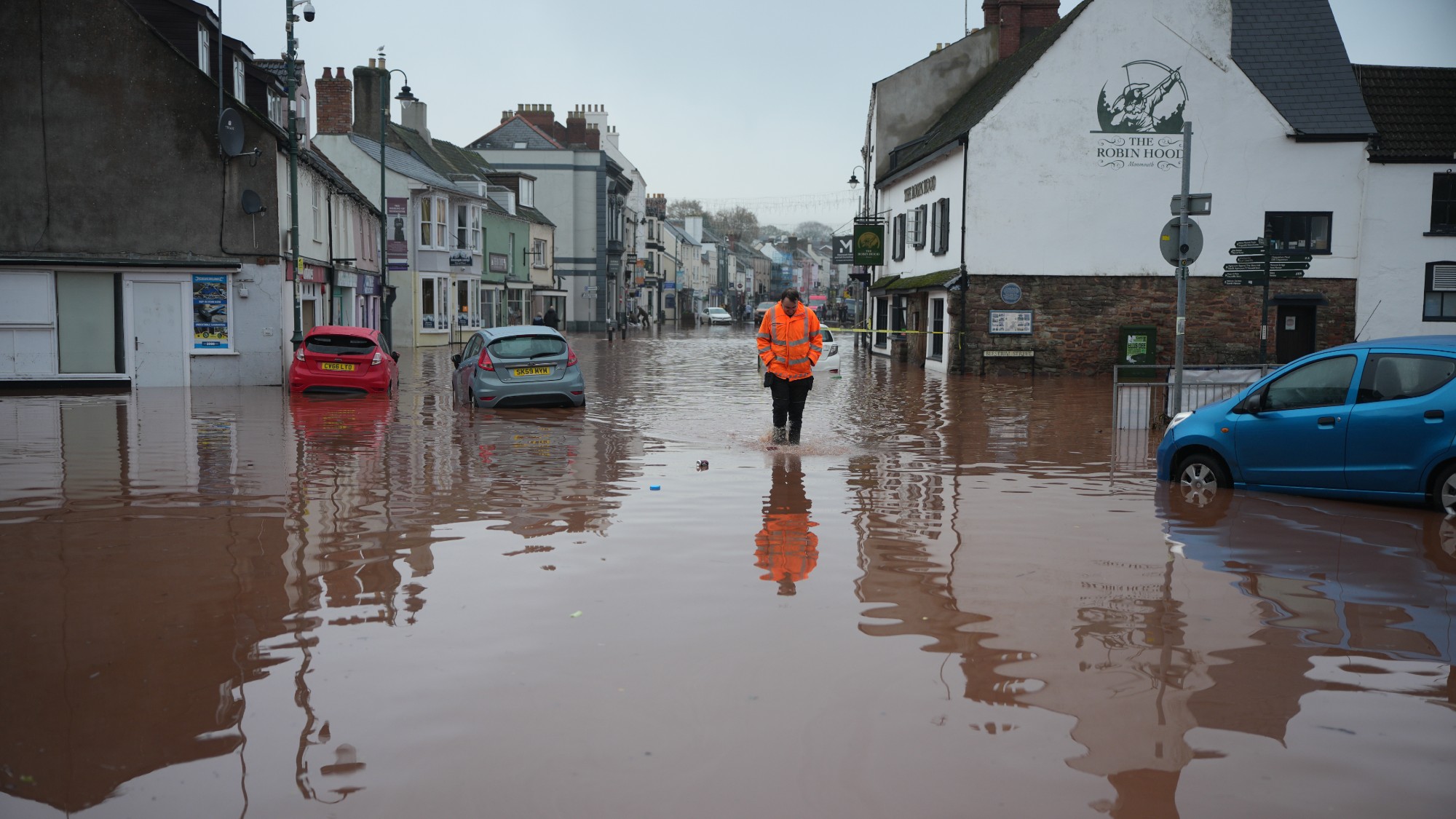 How will climate change affect the UK?
How will climate change affect the UK?The Explainer Met Office projections show the UK getting substantially warmer and wetter – with more extreme weather events
